Budget 2016-17
has been presented in Parliament. The Finance Minister has kept the
Personal Income Tax slab rates unchanged for the Financial Year 2016-17 (Assessment Year
2017-2018).
He has proposed to
introduce or extend the Tax Deduction limits under few Sections of the Income
Tax Act.
Download Automated Master of Form 16 Part A&B for Financial Year 2015-16 and Assess Year 2016-17 [This Excel Based Utility can prepare at a time 100 employees Form 16 Part A & B for F.Y.2016-17]
Let
us understand all the important sections and new proposals with respect to Income Tax Deductions FY 2016-17. This list can help
you in planning your taxes.
Income
Tax Deductions FY 2016-17
Section 80c
The
maximum tax exemption limit under Section 80C has been retained as Rs 1.5 Lakh
only. The various investment avenues or expenses that can be claimed as tax
deductions under section 80c are as below;
- PPF (Public Provident Fund)
- EPF (Employees’
Provident Fund)
- Five year Bank or Post office Tax saving Deposits
- NSC (National
Savings Certificates)
- ELSS Mutual Funds (Equity Linked Saving Schemes)
- Kid’s Tuition Fees
- SCSS (Post office Senior Citizen
Savings Scheme)
- Principal repayment of Home Loan
- NPS (National
Pension System)
- Life Insurance Premium
- Sukanya Samriddhi
Account Deposit Scheme
Section 80CCC
Contribution
to annuity plan of LIC (Life Insurance Corporation of India
Section 80CCD
Employee
can contribute to Government notified Pension Schemes (like
National Pension Scheme – NPS). The contributions can be upto 10% of the salary
(or) Gross Income and Rs 50,000 additional tax benefit u/s 80CCD (1b) was
proposed in Budget 2015.
To
claim this deduction, the employee has to contribute to Govt recognized Pension
schemes like NPS. The 10% of salary limit is applicable for salaried
individuals and Gross income is applicable for non-salaried. The definition of
Salary is only ‘Dearness Allowance.’ If your employer also contributes to
Pension Scheme, the whole contribution amount (10% of salary)can be claimed as tax deduction under
Section 80CCD (2).
Kindly
note that the Total
Deduction under section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD(1) together cannot exceed Rs 1,50,000 for the financial year 2016-17.
The additional tax deduction of Rs 50,000 u/s 80CCD (1b) is over and above this
Rs 1.5 Lakh limit.
Section 80D
Deduction
u/s 80D on health insurance premium is Rs 25,000. For Senior Citizens it
is Rs 30,000. For very senior citizen above the age of 80 years who are not
eligible to take health insurance, deduction is allowed for Rs 30,000 toward
medical expenditure.
Preventive health checkup (Medical checkups) expenses to the extent of Rs 5,000/- per family can be claimed as tax deductions. Remember, this is not over and above the individual limits as explained above. (Family includes: Self, spouse, dependent children and parents).
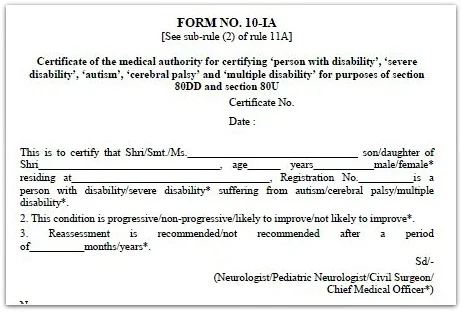
Section 80DD
You
can claim up to Rs 75,000 for spending on medical treatments of your dependents (spouse, parents, kids or siblings) who have 40% disability. The tax deduction limit
of up to Rs 1.25 lakh in case of severe disability can be availed.
Section 80DDB
An
individual (less than 60 years of age) can claim upto Rs 40,000 for the treatment of specified
critical ailments. This can also be claimed on behalf of the dependents. The
tax deduction limit under this section for Senior Citizens is Rs 60,000 and for
very Senior Citizens (above 80 years) the limit is Rs 80,000.
To
claim Tax deductions under Section 80DDB, it is mandatory for an individual to
obtain ‘Doctor Certificate’ or ‘Prescription’ from a specialist working in a
Govt or Private hospital.
For
the purposes of section 80DDB, the following shall be the eligible diseases or
ailments:
- Neurological Diseases where the disability level has
been certified to be of 40% and above;
(a)
Dementia
(b) Dystonia Musculorum Deformans
(c) Motor Neuron Disease
(d) Ataxia
(e) Chorea
(f) Hemiballismus
(g) Aphasia
(h) Parkinson’s Disease
(b) Dystonia Musculorum Deformans
(c) Motor Neuron Disease
(d) Ataxia
(e) Chorea
(f) Hemiballismus
(g) Aphasia
(h) Parkinson’s Disease
- Malignant Cancers
- Full Blown Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) ;
- Chronic Renal failure
- Hematological disorders
- Hemophilia
- Thalassaemia
Section 24 (B)
The
interest component of home loans is allowed as deduction under Section
24B for up to Rs 2 lakh in case of a self-occupied house. If your property is a
let-out one then the entire interest amount can be claimed as tax deduction. Section 80EE
This
is a new proposal which has been made in Budget 2016-17. First time Home
Buyers can claim an additional Tax deduction of up to Rs 50,000 on home
loan interest payments u/s 80EE. The below criteria has to be met for claiming
tax deduction under section 80EE.
- The home loan should have been sanctioned in FY 2016-17.
- Loan amount should be less than Rs 35 Lakh.
- The value of the house should not be more than Rs 50
Lakh &
- The home buyer should not have any other existing
residential house in his name.
Section 80U
This
is similar to Section 80DD. Tax deduction is allowed for the tax assessee who
is physically and mentally challenged.
Section 80GG
As
per the budget 2016 proposal, the Tax Deduction amount under 80GG has
been increased from Rs 24,000 per annum to Rs 60,000 per annum. Section
80GG is applicable for all those individuals who do not own a residential house
& do not receive HRA (House
Rent Allowance).
The
extent of tax deduction will be limited to the least amount of the following;
- Rent paid minus 10 percent the adjusted total income.
- Rs 5,000 per month.
- 25 % of the total income.
Section 80G
Contributions
made to certain relief funds and charitable institutions can be claimed as a
deduction under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act. This deduction can only be
claimed when the contribution has been made via cheque or draft or in cash. But
deduction is not allowed for donations made in cash exceeding Rs 10,000.
In-kind contributions such as food material, clothes, medicines etc do not
qualify for deduction under section 80G.
Section 80E
If
you take any loan for higher studies (after completing Senior Secondary
Exam), tax deduction can be claimed under Section 80E for
interest that you pay towards your Education Loan. This loan should have been
taken for higher education for you, your spouse or your children or for a
student for whom you are a legal guardian. Principal Repayment on educational loan
cannot be claimed as tax deduction.
There
is no limit on the amount of interest you can claim as deduction under section
80E. The deduction is available for a maximum of 8 years or till the interest
is paid, whichever is earlier.
Section 87A Rebate
If
you are earning below Rs 5 lakh, you can save an additional Rs 3,000 in
taxes. Tax rebate under Section 87A has been raised from Rs 2,000 to Rs 5,000
for FY 2016-17 (AY 2017-18).
In
case if your tax liability is less than Rs 5,000 for FY 2016-17, the rebate u/s
87A will be restricted up to income tax liability only.
Section 80 TTA
Deduction
from gross total income of an individual or HUF, up to a maximum of Rs.
10,000/-, in respect of interest on deposits in savings account with a bank,
co-operative society or post office can be claimed under this section. Section
80TTA deduction is not available on interest income from fixed
deposits.