Tax Exemption on Interest U/s 80TTA | We all have a tendency to check the amount of interest earned
on savings accounts during the year, but do we know how this interest is calculated and the tax on
interest on savings accounts that is due? In this article, we will try to give you an idea of such points
and interest tax deductions under section 80TTA.
Savings account interest rate
Previously, the RBI set interest rates on savings accounts at 4% per year. These interest rates were controlled by the RBI and all banks were required to pay the same interest rates regardless of the amount of money held by the Bank.
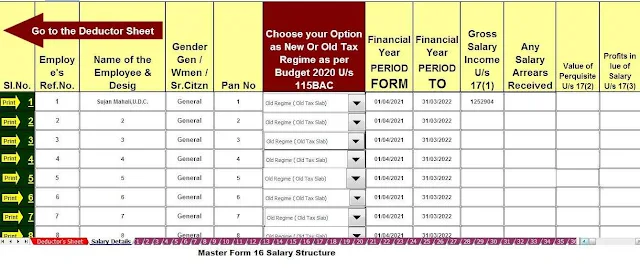
Download and Prepare One by One Auto Fill Income Tax Form 16
Part A&B for the F.Y.2021-22
But on October 25, 2011, the RBI deregulated this interest rate-setting system. This deregulation meant that all banks were now free to set the interest rates payable. This resulted in different banks paying different interest rates, which is how it should be in a free economy.
Furthermore, RBI said that banks can also choose to pay differentiated interest rates, which means that they can pay a different interest rate if the amount is less than Rs. 1,000,000 rubles and miscellaneous interest on Rs. 100000.
After this interest rate deregulation announcement, different banks started paying different interest rates. To encourage more customers to open savings accounts at their banks, banks also started offering higher interest rates on savings accounts, which ultimately benefited the customer. From the 4% per year paid on savings accounts before deregulation, interest rates have risen significantly, with some banks paying as much as 6-7% per year.
Download and Prepare One by One Auto Fill Income Tax Form 16 Part B for the F.Y.2021-22
Another change that has taken place since the deregulation of interest rates concerns the way interest is calculated. Previously, interest was accrued on the minimum balance of funds in a bank account within a month. Therefore, if I had Rs. 90,000 in his bank account for the whole month and for 1 day the balance was Rs. 10,000, you will only be paid interest on Rs. 10,000 and not Rs. 90,000 (a simple example was taken for understanding).
But now this has changed and interest is paid daily on the account balance at the end of the day. This has once again benefited clients as they will now earn more interest not only due to the higher interest rates, but also the change in the way they are calculated.
Tax on interest on savings accounts
Interest on savings accounts was previously taxed at flat rates. But as of April 1, 2012, there was an amendment to the Income Tax Law and a deduction of Rs. 10,000 is allowed under Section 80TTA for interest earned in the tax year on deposits of
Save a bank account
Cooperative bank
The amount earned in excess of this amount, Rs. 10,000 will be taxed according to income tax rates. This Section 80TTA deduction is only available to individuals and HUF and is in excess of Section 80C deductions.
The taxpayer is asked to note that this is a deduction, not an exemption. Therefore, it will first be included in the taxpayer's total income and then allowed as a deduction under Chapter VI-A.
The difference between the interest on a savings account and a fixed-term deposit
With a fixed deposit, you must deposit the amount in the bank over a certain period, while with a savings account, you can withdraw the amount at any time. Since the amount of a term deposit is kept in banks for a certain period, it pays a higher interest compared to the interest on a savings account.
Download and Prepare at a time 50 Employees Auto Fill Income Tax Form 16 Part B for the F.Y.2021-22
However, deductions for interest received on a fixed-term deposit are not allowed and are taxed at the individual beneficiary's income tax rates. In addition, TDS @ 10% is also deducted from fixed deposit interest if the interest earned is more than Rs. 10,000.
On the other hand, a deduction of Rs. 10,000 is given for interest on savings accounts. Also, no TDS will be deducted from the savings account interest, regardless of the amount of interest earned. Interest income (whether from a savings account or a time deposit) is disclosed in Income from other sources.
Even though the deduction is Rs. The 10,000 is for interest on a savings account and not on time deposits, however, time deposits are desirable because the interest paid on time deposits is much higher than the interest paid on a savings account.
The PPF account is also a good investment option for those who are interested.