Under Section 89(1) as per the Income Tax Act 1961:
Understanding Income Tax Arrears Relief Calculation U/s 89(1) with Form 10E | According to the Income Tax Law, a person must pay taxes on their income earned in a fiscal year. However, there may be cases where an employee has received back or anticipated wages from a prior financial year. In these cases, the employee's tax liability may increase significantly due to the tax slab rates. To provide relief in such cases, the Income Tax Act 1961 has a provision in Section 89(1).
Understanding U/s 89(1) of the Income Tax
Act 1961?
Section 89(1) of the Income Tax Act 1961 grants an exemption to an employee who has earned back or anticipated wages in a financial year relating to a prior financial year. The section provides relief by computing the tax payable on the employee's total income in the fiscal year in which the wage arrears or advances are received as if such income had been received in the year or years to which it relates.
Conditions that must be met to claim
relief under Section 89(1)
To claim an exemption under Section 89(1), an employee must meet the following conditions:
The employee must have received salary arrears or advances in a fiscal year, which belongs to a previous fiscal year.
The worker must have received a salary or pension in the year in which the delayed or advanced wages were received.
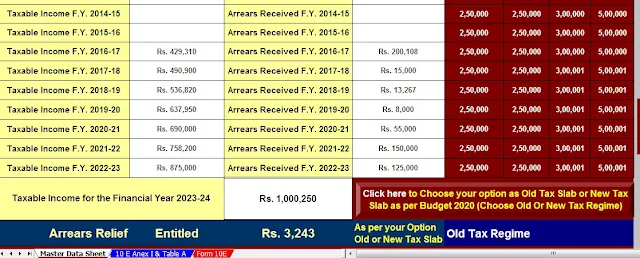
The employee must provide Form 10E to their employer for the calculation of benefits under Section 89(1).
Section 89(1) Calculation Wages The Section 89(1) exemption is calculated by dividing wages in arrears or in advance by the number of years to which they relate. The amount thus obtained is added to the worker's income for the year in which the salary in arrears or advance is received. The tax payable on the total income is then calculated according to the rates applicable to the year in which the salary arrears or advances are received.
Example Suppose an employee has received back wages of Rs 5,00,000 in FY 2022-23 which refers to FY 2019-20. Employee income for FY 2022-23 excluding arrears is Rs 6,00,000. The exemption under Section 89(1) shall be calculated as follows:
Back wages = Rs 5,00,000
Number of Years to which it refers = 2 (The years 2019-20 and 2020-21)
Delays divided by the number of years = Rs 2,50,000
Total revenue for FY 2022-23 = Rs 8,50,000 (Rs 6,00,000 + Rs 2,50,000)
Tax payable on total income = Rs 22,500 (based on applicable rates for the fiscal year 2022-23)